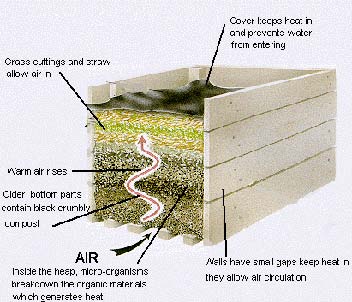
What is Composting?
Decomposition similar to composting occurs throughout nature as waste dissolves in the absence of all the conditions that modern composters talk about; however, the process can be slow. For example, in the forest bark, wood and leaves break down into humus over several years.
In restricted environments, for example, vegetables in a plastic trash container, decomposition with a lack of air encourages growth of anaerobic microbes, which produce disagreeable odors. Another form of degradation practiced deliberately in absence of oxygen is called anaerobic digestion ‐an increasingly popular companion to composting as it enables capture of residual energy in the form of biogas, whereas composting releases the majority of carbon‐energy as a gas, which can be used for cooking or lightening.